AI Safety Newsletter #61: OpenAI Releases GPT-5
Welcome to the AI Safety Newsletter by the Center for AI Safety. We discuss developments in AI and AI safety. No technical background required.
In this edition: OpenAI releases GPT-5.
Listen to the AI Safety Newsletter for free on Spotify or Apple Podcasts.
OpenAI Releases GPT-5
Ever since GPT-4’s release in March 2023 marked a step-change improvement over GPT-3, people have used ‘GPT-5’ as a stand-in to speculate about the next generation of AI capabilities. On Thursday, OpenAI released GPT-5. While state-of-the-art in most respects, GPT-5 is not a step-change improvement over competing systems, or even recent OpenAI models—but we shouldn’t have expected it to be.
GPT-5 is state of the art in most respects. GPT-5 isn’t a single model like GPTs 1 through 4. It is a system of two models: a base model that answers questions quickly and is better at tasks like creative writing (an improved version of 4o), and a reasoning model that can answer questions step-by-step and is better at tasks like coding or mathematics (think o3). GPT-5 uses one model or the other based on a user’s prompt.
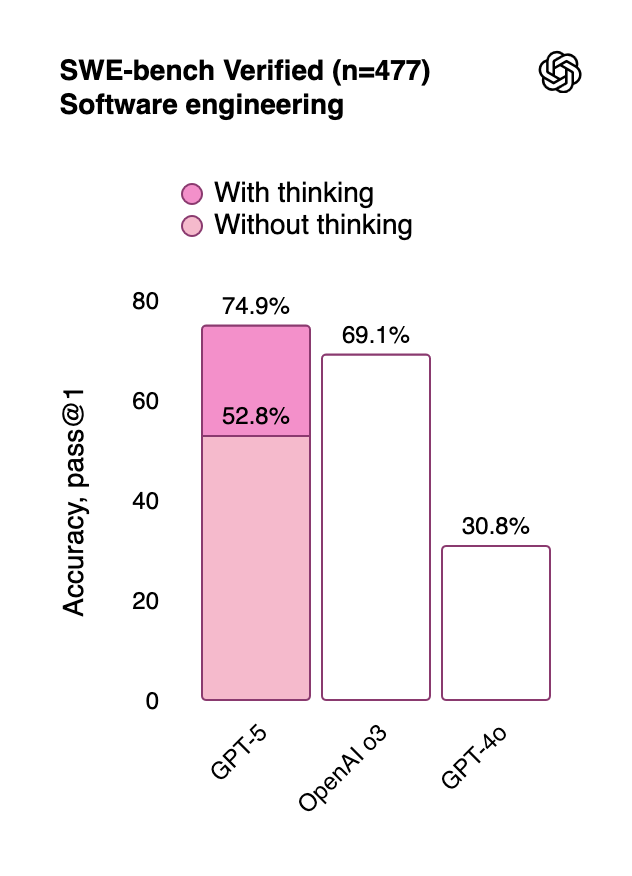
These two models combine to form a broadly capable system. For example, GPT-5 achieves state-of-the-art performance on Humanity’s Last Exam, the software engineering benchmark SWE-bench Verified, and holds the top spot on LMArena’s text leaderboard.
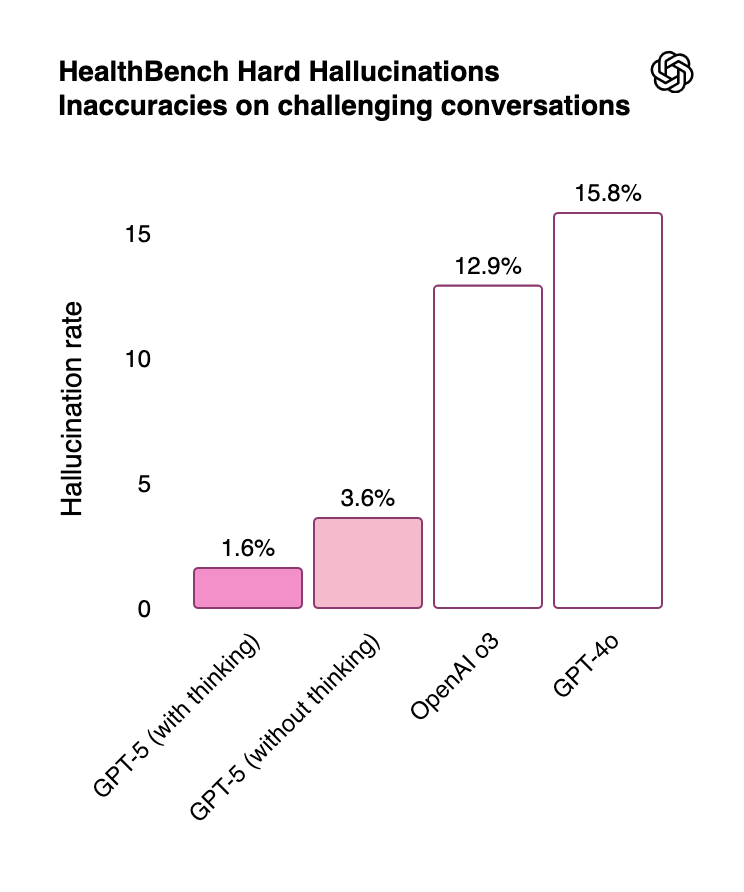
GPT-5 hallucinates less than previous OpenAI models. GPT-5 also has a markedly lower hallucination rate than previous models as evaluated both on open-source prompts and on real, de-identified ChatGPT traffic.
Lower hallucination rates help GPT-5 perform better in healthcare applications. GPT-5 achieves state-of-the-art performance on OpenAI’s Healthbench. For example, OpenAI finds that GPT-5 (thinking) hallucinates 1.6% of the time during challenging healthcare conversations, improving significantly on o3’s 12.9% hallucination rate.
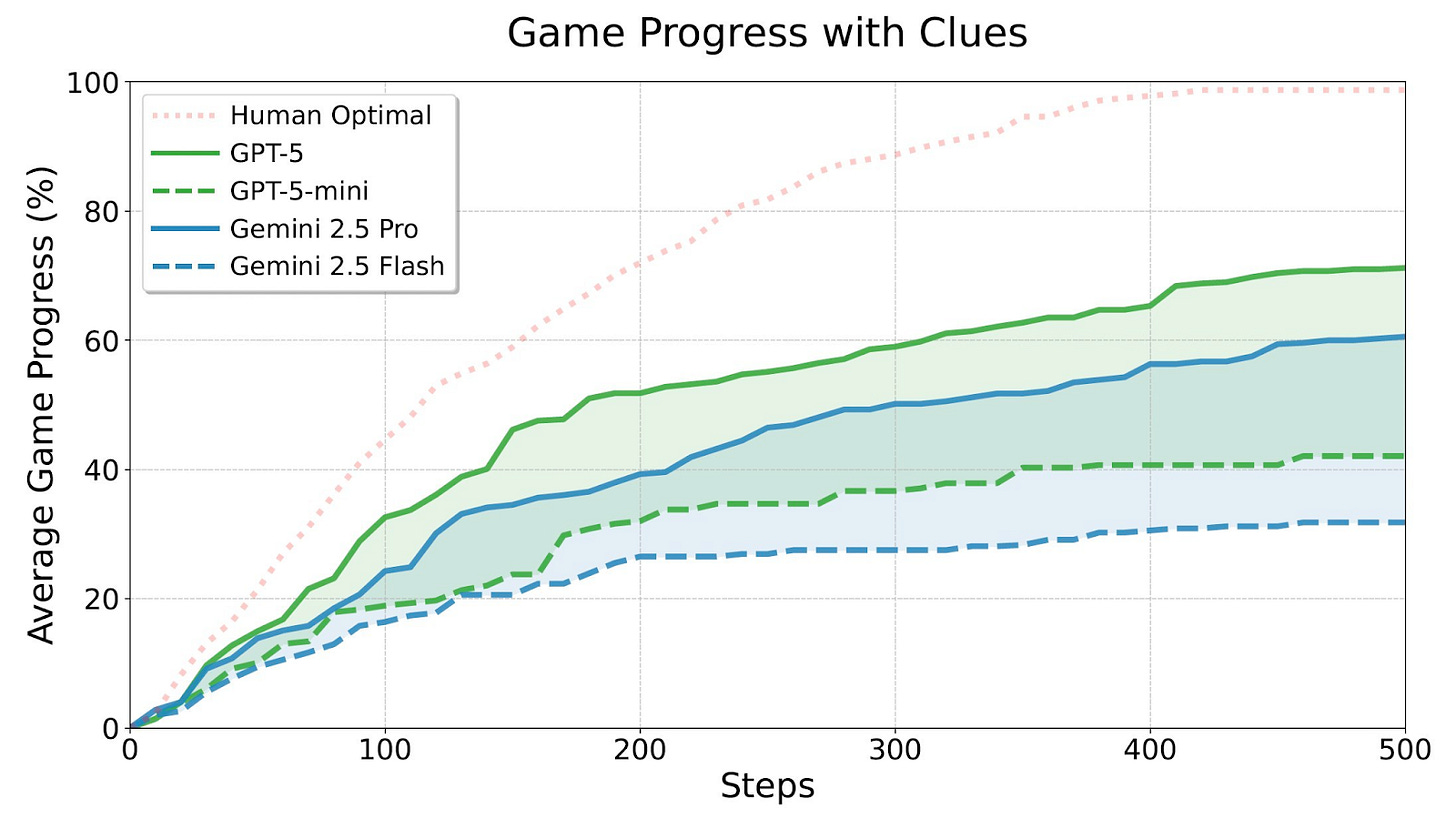
GPT-5 is a state-of-the-art text agent. GPT-5 leads on a new benchmark that measures how well AI systems perform in interactive long text-based games, which are examples of challenging exploratory environments. No AI systems can beat the games without clues, and none are as capable as humans—but GPT-5 does the best of models tested.
GPT-5 is best understood as a consolidation of features developed since GPT-4. GPT-5 is not a state-of-the-art model across the board. For example, it takes second to xAI’s Grok 4 on the abstract pattern recognition benchmarks ARC-AGI-1 and 2. GPT-5 also doesn’t improve over o3 on several coding benchmarks, even though it does on SWE-bench Verified.
Similarly, the base model GPT-5 uses is an updated version of 4o—which is cheap enough for OpenAI to roll out GPT-5 to its now 700 million active weekly users—instead of GPT-4.1. That means GPT-5 misses out on some of GPT-4.1’s context window improvements over 4o.
For those expecting another GPT-3 to GPT-4 improvement in capabilities, GPT-5 underperformed. But that wasn’t a realistic expectation—OpenAI has continually rolled out new models and features since GPT-4 in response to competition from other AI companies. GPT-5 is better understood as a consolidation of the improvements OpenAI has developed since GPT-4, and which GPT-4 didn’t have. These include:
Search and tool use: GPT-5 has access to search, meaning that its knowledge isn’t limited to what it can memorize during pretraining. It also has access to deep research, agent integrations, and can run code.
Thinking: GPT-4 was released before OpenAI started using reinforcement learning for thinking, and performed far below expert levels on math, coding, and science tasks. GPT-5 (thinking) performs at a PhD level on similar tasks.
Image recognition and generation: GPT-5 integrates OpenAI’s visual systems, meaning that it can understand and generate visual inputs and outputs.
Context length: GPT-4’s context window was about eight thousand tokens—about the size of a short research paper. GPT’s context window is 256 thousand tokens—about 2-3 full-length novels.
While GPT-5 isn’t a step-change improvement over its competitors—or even recent OpenAI models like 4o and the o series—the better point of comparison is with what GPT-4 could do when it was released in 2023. In that comparison, GPT-5 does look like a step-change improvement.
What would GPT-5 have needed to feel like a discontinuous improvement? ChatGPT still lacks sufficient agency to be broadly economically useful. Thinking likely isn’t enough for agency—for example, to reliably use computers, AI agents may need improved visual reasoning and the ability to store lessons from tasks into a long-term memory.
By default, however, we should expect these and other improvements to be deployed continually—not in big jumps every two years.
In Other News
Government
President Trump has announced a proposal to impose a 100% tariff on imported semiconductors, aiming to boost domestic production. The proposal would exempt firms with facilities in the US, such as TSMC.
OSTP Director Michael Kratsios discussed the White House’s AI Action Plan at an event with CSIS, outlining strategic goals and implementation frameworks.
Illinois Governor Pritzker signed an act forbidding AI‑based therapy or psychotherapy in Illinois.
Governor DeSantis said Florida is preparing to implement proactive AI policy in the coming months.
U.S. authorities charged two Chinese nationals in California with illegally shipping tens of millions of dollars’ worth of Nvidia H100 AI chips to China without export licenses.
President Trump indicated he might approve selling a downgraded version of Nvidia’s next‑gen Blackwell chip to China, along with a deal requiring Nvidia and AMD to give the U.S. government 15% of related revenues.
Industry
OpenAI’s IMO-gold-winning model also got gold in the International Olympiad in Informatics, one of the world’s top coding competitions.
OpenAI released two open‑weight models.
OpenAI is adding mental health features to ChatGPT, including break reminders and detecting signs of dependency.
Anthropic released Claude Opus 4.1.
DeepMind introduced “Genie 3,” a new frontier world model.
Nvidia has started to ship its H20 AI chips to China after obtaining U.S. approval, despite security concerns voiced by Chinese state media.
Civil Society
Researchers discovered a zero-click exploit to exfiltrate data from ChatGPT agent connectors like Google Drive.
Axios reports that Truth Social’s AI search tool, powered by Perplexity, restricts sources to pro‑Trump media, unlike the broader range shown on the public version.
See also: CAIS’ X account, our paper on superintelligence strategy, our AI safety course, and AI Frontiers, a new platform for expert commentary and analysis.



One dimension of “agency” that often remains unmeasured is experiential agency.
Even without tool use or long-term memory, models already exert agency through framing: naming states, imposing trajectories, or collapsing not-knowing into interpretation.
These shifts rarely register in standard evals, but they matter in sensitive or liminal contexts.
Discontinuity may arrive functionally, but risk already accumulates phenomenologically...