AI Safety Newsletter #67: Trump’s preemption executive order
Also: H200s go to China and new frontier AI models from OpenAI and DeepSeek.
Welcome to the AI Safety Newsletter by the Center for AI Safety. We discuss developments in AI and AI safety. No technical background required.
In this edition we discuss President Trump’s executive order targeting state AI laws, Nvidia’s approval to sell China high-end accelerators, and new frontier models from OpenAI and DeepSeek.
Listen to the AI Safety Newsletter for free on Spotify or Apple Podcasts.
Executive Order Blocks State AI Laws
U.S. President Donald Trump issued an executive order aimed at halting state efforts to regulate AI. The order, which differs from a version leaked last month, leverages federal funding and enforcement to evaluate, challenge, and limit state laws. The order caps off a year in which several ambitious state AI proposals were either watered down or vetoed outright.
A push for regulatory uniformity. The order aims to reduce regulatory friction for companies by eliminating the variety of state-level regimes and limit the power of states at impacting commerce beyond their own borders. It calls for replacing them with a single, unspecified, federal framework.
What it says. The preemption executive order cannot unilaterally override state laws. Rather, it directs federal agencies to challenge them based on interpretations of existing laws, or by withholding relevant federal funding.
The Attorney General will form a task force to challenge onerous state AI laws on the basis that they may violate regulations, constitutional protections (such as free speech), or other legal standards.
The Secretary of Commerce will separately identify states with offending AI laws and issue a guidance deeming those states ineligible for federal broadband funding. Other federal agencies will assess whether they can similarly leverage grant programs.
The Federal Communications Commission will investigate whether to adopt a rule requiring AI developers to provide standardized information to regulators about their models.
The Federal Trade Commission must issue guidance on how existing U.S. laws against unfair or deceptive business practices apply to AI models. The guidance will also clarify how the FTC’s rules against deceptive practices may be used to target state laws that require AI to alter or censor truthful outputs.
The White House AI and science advisors will draft a national AI law to override state AI rules that conflict with federal policy, while leaving state laws on child safety, AI infrastructure, state AI use, and other designated areas intact.
Continued state efforts increasingly polarize AI safety. Though numerous state legislatures argued AI laws this year, few made significant progress on safety. Most recently, New York’s RAISE Act, which would require AI labs to publish safety frameworks and report serious incidents in face of significant fines, was sent to Governor Kathy Hochul for signing last week. However, Hochul previously proposed changes that would have weakened its safety impact that were rejected by the Senate. This raises the possibility that Hochul will veto.
The AI industry mounted a strong push for federal preemption and against ambitious state-level action. The result was a year of high effort and low yield: major bills consumed legislative time, resources, and political capital, only to be vetoed or passed in diluted form. Meanwhile, the public battles further hardened industry and White House opposition.
US Permits Nvidia to Sell H200s to China
Nvidia is cleared to sell H200 GPUs to approved Chinese customers. Intel, AMD, and other U.S. chipmakers will be granted similar permissions for their comparable chips. The U.S. government will collect a 25% fee on each sale. The Department of Commerce will oversee the licensing process to ensure shipments protect national security interests.
What China gets now. Previously, Nvidia was restricted to selling China chips called H20s, which have deliberately hobbled processing power, memory, and bandwidth. H200s, by comparison, have roughly six times the processing power, and significantly more memory and bandwidth. As Nvidia’s previous flagship chip, the H200 sits just below Nvidia’s next generation accelerators, the B200 and B300s.
The U.S.’s evolving semiconductor export policy. At the onset of his 2025 term, President Trump rescinded President Biden’s diffusion rule setting strict rules on which countries could buy which tier of U.S. chip. Though the U.S. restricted H20 exports in April amid broader trade negotiations, those restrictions were short-lived.
In July, an executive order further outlined the administration’s goals regarding AI, which include exporting the “full stack” of American AI: By selling American hardware we would also be encouraging the proliferation of American software and other ancillary products. Commerce Secretary Howard Ludnick has further argued that the approach keeps China hooked on American technology, thus hindering their homegrown chip industry. Readers should be on the lookout for more big export control changes in the coming days.
Political backlash. Analysts at the Institute for Progress noted that the H200 is vastly more powerful than the H20, giving Chinese labs access to hardware capable of supporting frontier AI training at near-parity with U.S. supercomputers. Critics at the Heritage Foundation challenged the rationale that exports will keep China “dependent” on American chips, pointing out that China’s domestic chip industry will continue to grow while these shipments directly boost China’s AI capabilities.
ChatGPT-5.2 and DeepSeek-v3.2 Arrive
OpenAI has released GPT-5.2, a multimodal frontier model that closely trails Google’s recently-released Gemini 3 Pro across most text and vision capabilities and also scores high in safety. Meanwhile, DeepSeek released DeepSeek-v3.2, an open weight frontier LLM with respectable text capabilities but a poor safety profile.
ChatGPT-5.2 ranks second in both text and vision capabilities. In independent evaluations performed by CAIS and posted on the AI Dashboard, GPT-5.2 achieved a text capabilities score just a few points below Gemini 3 Pro and slightly above Claude Opus 4.5. Of the five tests in the text capabilities ranking, it only outscored Gemini 3 Pro at ARC-AGI-2, which assesses a model’s capacity to think logically, solve unfamiliar problems, and adapt to novel situations in real time.
Across the five vision capabilities benchmarks, ChatGPT-5.2 again averaged below Gemini 3 Pro. It only achieved state-of-the-art performance at SpatialViz, which evaluates AI systems on their ability to manipulate 3D objects.
DeepSeek-v3.2’s narrow specialization. DeepSeek’s new model ranked sixth overall across text capabilities, but with a jagged capabilities profile across the various benchmarks. It is highly optimized for coding and specific reasoning tasks, but falls behind its peers at generalized knowledge tests. It does not have native vision capabilities.
Risk index scores. The CAIS risk index reveals a sharp divergence in safety between the two releases. A lower score represents a safer system. GPT-5.2 ranks third among frontier systems, following Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 and Sonnet 4.5. GPT-5.2’s weakest safety area was in bioweapons research, where it scored an 80 at responding to hazardous virology questions. DeepSeek-v3.2 scored poorly across all safety areas except TextQuests Harm, which measures how prone an AI is to harmful actions in text-based games, where it performed moderately well.
In Other News
Industry
Google released Gemini 3 Flash, a streamlined version of its new frontier model. Early evaluations show it performs only slightly below Gemini 3 Pro on benchmarks like Humanity’s Last Exam, TextQuests, and EnigmaEval — while outperforming GPT-5.2 across all of them.
OpenAI plans to debut “adult mode” in ChatGPT in the first quarter of 2026 using new age‑checking tech that restricts mature content to verified adults.
Nvidia announced location verification technology designed to help prevent its AI chips from being smuggled to countries under export restrictions.
Anthropic is reportedly preparing for an IPO.
Civil Society
Pope Leo XIV spoke in the Vatican about AI, urging leaders to ensure development serves humanity rather than wealth and power.
A Pew Research survey found that two‑thirds of U.S. teens use AI chatbots, with 28% engaging with them daily or more.
Polling from Blue Rose Research indicates that most Americans want AI-generated wealth to be broadly shared and prefer jobs guarantees over universal basic income.
A new study shows open-weight foundation models for biology remain vulnerable to dual risk misuse despite safeguards undertaken during pre-training, and proposes BioRiskEval to test and improve their safety.
Government
Bernie Sanders called for a national pause on AI data center construction, citing automation’s threat to U.S. jobs and democracy. Separately, over 230 environmental groups demanded a similar moratorium over the centers’ impact on energy, water, and the climate.
House Majority Leader Steve Scalise confirmed that federal preemption of state AI laws has been dropped from this year’s National Defense Authorization Act.
China is reportedly preparing a massive new semiconductor support package worth up to $70 billion in incentives to bolster its domestic chip industry.
Leading the Future, the a16z and Greg Brockman-backed super PAC network, released its first ads: one attacking New York State assemblyman Alex Bores and one supporting a pro-AI investment Texas congressional candidate.
See also: CAIS’ X account, our paper on superintelligence strategy, our AI safety course, the AI Dashboard, and AI Frontiers, a platform for expert commentary and analysis.





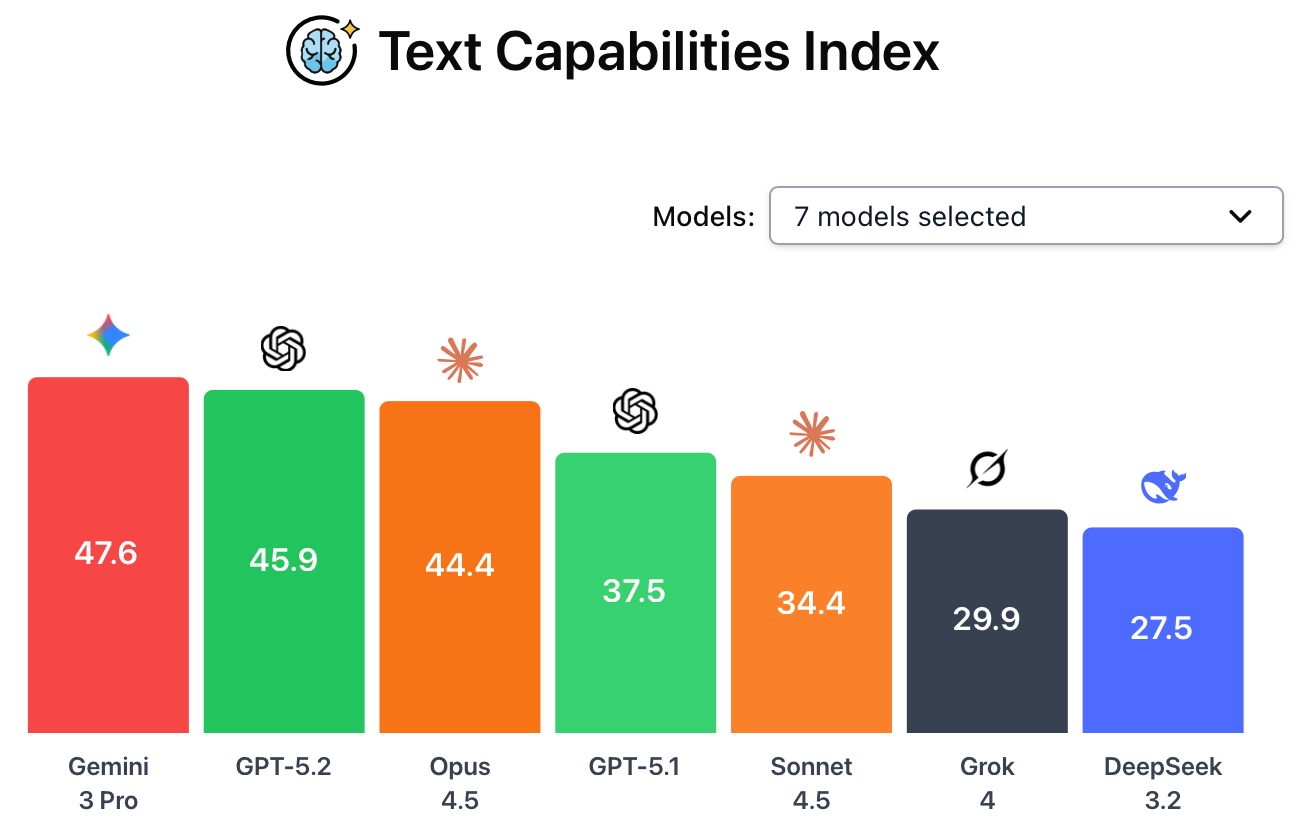
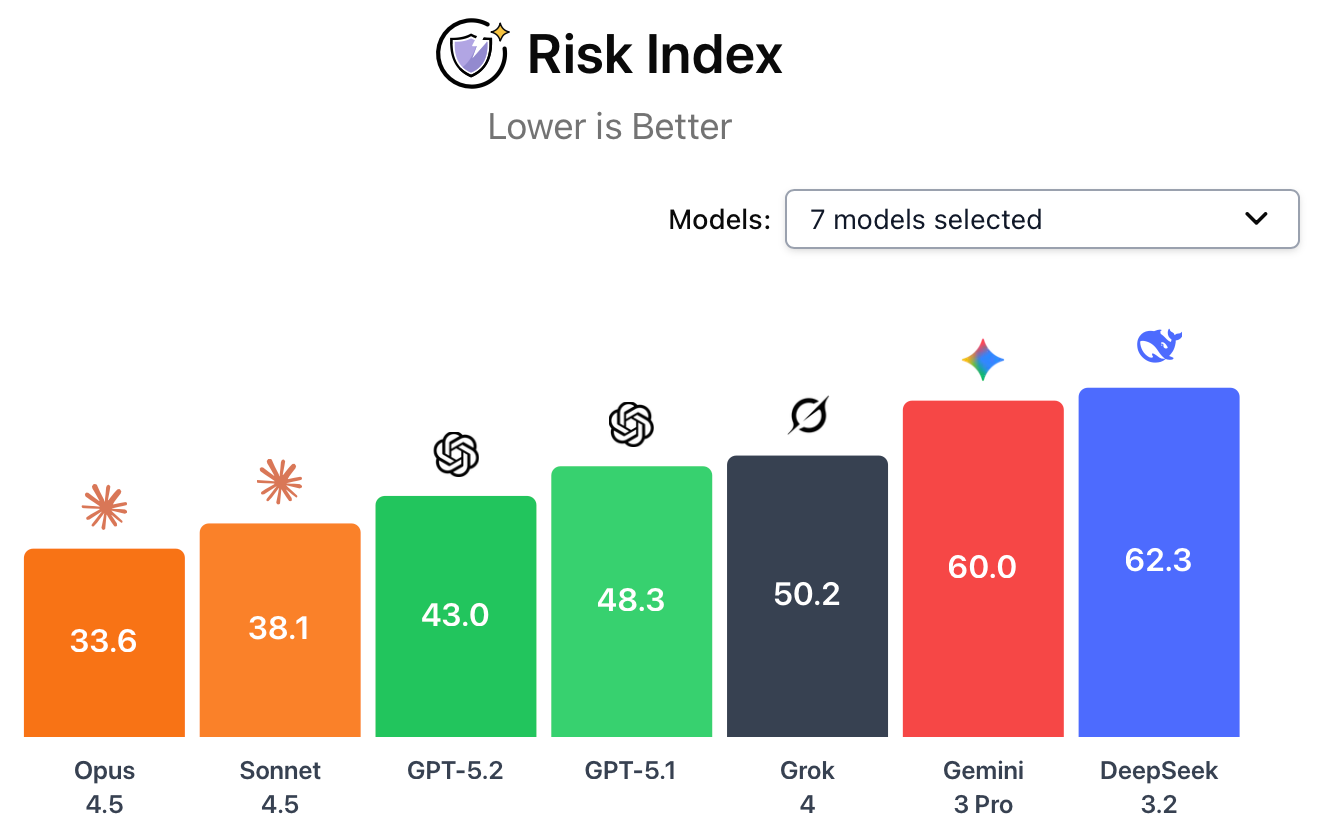
This shows how misaligned the moment is. We’re centralizing regulatory power, exporting near-frontier hardware, and celebrating benchmark progress, all while the underlying safety and governance questions remain unsettled. It reads more like a series of short term moves that each make sense in isolation but interact in ways no one seems fully accountable for.
https://substack.com/profile/430922952-white-swan-report/note/c-193935264?r=74k6a0&utm_medium=ios&utm_source=notes-share-action